Cable size calculations are essential in electrical and electronic engineering to determine the appropriate size or gauge of electrical cables required for a specific application. The cable size is crucial to ensure the safe and efficient transmission of electrical power while minimizing losses and maintaining safety standards. Here are the key factors and considerations in cable size calculations:
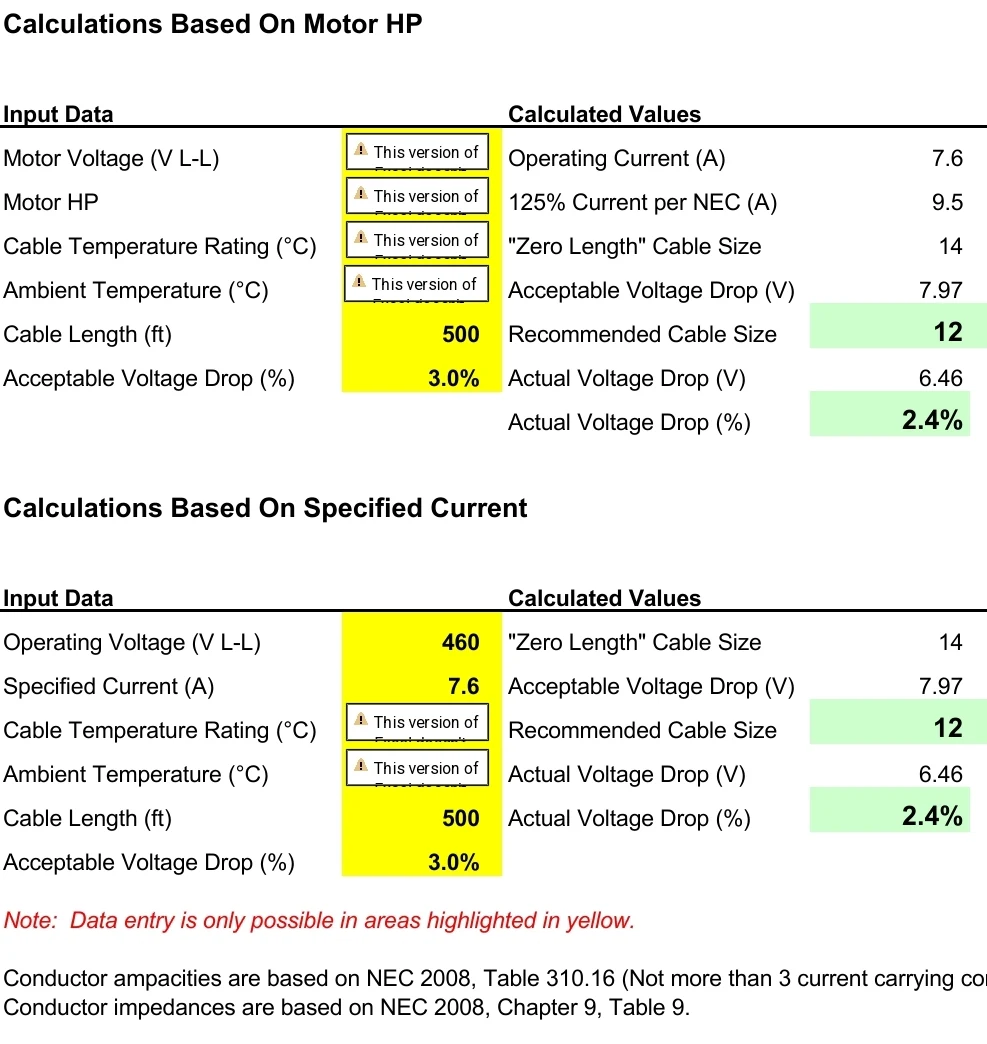
Current Carrying Capacity: The cable size should be selected to handle the maximum current that will flow through it without overheating. This is typically determined by the expected load and the type of conductor material (copper or aluminum).
Voltage Drop: Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage along the length of the cable. Excessive voltage drop can lead to inefficient power transmission and affect the performance of connected devices. Cable size must be chosen to limit voltage drop to an acceptable level.
Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the cable's environment can affect its current-carrying capacity. Cables in high-temperature environments may need to be larger to safely carry the same current.
Conductor Material: Copper and aluminum are the most common conductor materials. Copper has better conductivity but is more expensive than aluminum. The choice of material impacts cable size calculations.
Cable Insulation: Different types of cable insulation have varying temperature ratings and electrical properties. The insulation material must be suitable for the application.
Cable Installation Method: The way the cable is installed, whether in conduit, underground, or in the open air, affects its current-carrying capacity and may necessitate different cable sizes.
Regulatory Standards: Adherence to local electrical codes and standards is essential for safety and compliance. These standards often provide guidelines for cable size selection.
Load Characteristics: The type of load (resistive, inductive, or capacitive) can impact cable size calculations, as it affects the power factor and the cable's ability to carry current effectively.
Short-Circuit Current Rating: The cable should be able to withstand short-circuit currents without damage. This is a crucial safety consideration.
Cable size calculations involve using mathematical formulas and tables to consider these factors and determine the appropriate cable size for a given application. It's important to work with qualified electrical engineers or professionals to ensure accurate and safe cable size selections. Using cables that are too small can result in overheating and potential fire hazards, while oversized cables can be costly and inefficient.